
The initial diagnosis modality of PVS was Doppler US on days 1, 3, and 7 after liver transplantation. In all patients, flow was confirmed by Doppler ultrasonography (US) to ensure no abnormalities after anastomosis of the vessels. In 4 transplantation patients, the length of the portal vein was short and the cadaveric iliac vein graft was inserted between the recipient and the donor. Portal vein anastomosis was performed with sufficient growth factor to avoid stenosis. Anastomosis of the portal vein during liver transplantation was achieved by the standard end-to-end technique.
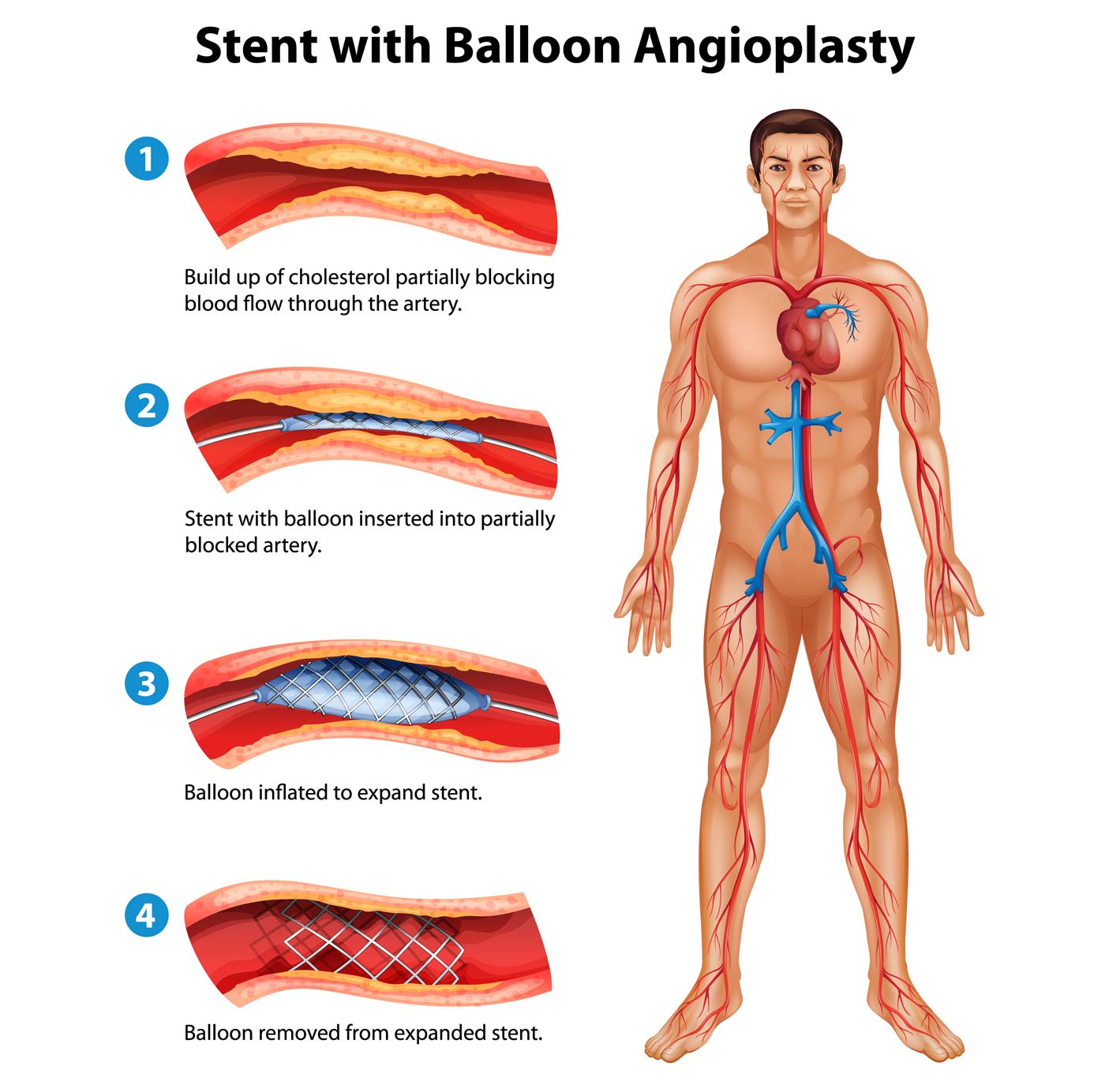
In LDLT, only the right liver was transplanted. In DDLT, the entire liver was used and was not split. The interval between transplantation and initial intervention ranged from 4 days to 49 months (mean, 15.4 months). These 31 patients ranged in age from 25 to 62 years (mean, 52 years) and included 28 men and 3 women. Of these patients, 31 patients underwent balloon angioplasty or stent insertion for PVS. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to identify appropriate treatment to reduce recurrence and excessive treatment of PVS by evaluating long-term outcomes of interventions in adult liver transplantation patients.Īt our institution 283 patients over 18 years of age underwent deceased donor liver transplantation (DDLT) and 1086 underwent LDLT between January 2001 and December 2015. In these circumstances, determining whether to perform balloon angioplasty or stent insertion in PVS patients is a difficult issue. In addition, stent insertion may result in excessive treatment for patients who may be adequately treated with balloon angioplasty alone. Although stent insertion has the advantage of low recurrence rate, it makes vascular anastomosis difficult at re-transplantation. For stent insertion, the reported recurrence rate was 0% ( 14, 15). Previous studies reported a recurrence rate of 26.7% ( 12) and 25.6% ( 13) for percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA). However, balloon angioplasty still has a higher recurrence rate than stent insertion. ( 8) published the first study on post liver transplantation portal vein angioplasty and stent insertion, percutaneous transhepatic balloon angioplasty and stent insertion have been commonly used and are considered safe methods to treat PVS after liver transplantation ( 9– 11). PVS is more common in living donor liver transplantations (LDLT) (4%) and pediatric liver transplantation (7% to 27%) ( 3, 5), but is uncommon (< 2%) in adult whole liver grafts ( 6, 7). Portal vein stenosis (PVS) is rare and occurs in 5% of all liver transplantations ( 4). Portal vein complications are anastomotic portal vein stenosis (PVS) or portal vein thrombosis ( 3). Portal vein reconstruction is the most important part of the surgery and portal vein complications can cause graft failure ( 2). Successful vascular anastomosis is an important factor for successful liver transplantation. Liver transplantation is considered the only treatment for end-stage liver disease ( 1).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
